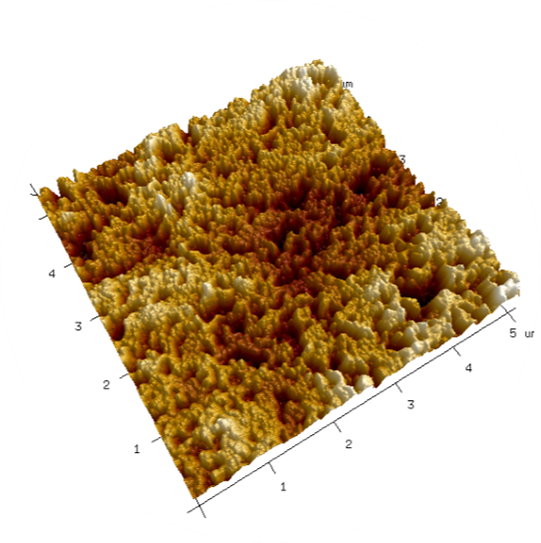
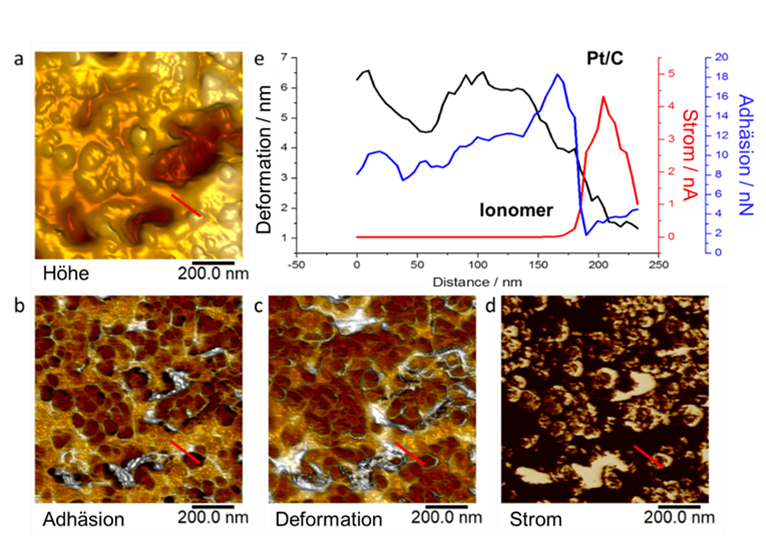
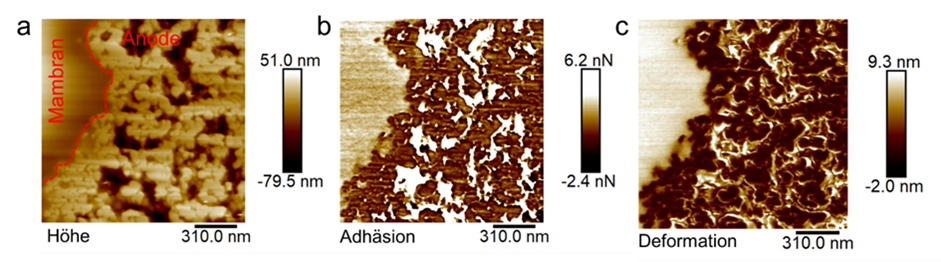
The key component of a Proton-Exchange Membrane (PEM) fuel cell is the membrane-electrode assembly (MEA). It consists of a solid state electrolyte, usually a film of Nafion®, a synthetic material, with electrodes mounted on both sides, in which the electro-chemical reactions take place. Investigating such catalytic membranes is a substantial part of the research work undertaken in the AFM Laboratory.
The illustration shows the topographical structure of such a membrane surface imaged with the AFM.